Towards replacing physical testing of granular materials with a Topology-based Model
Aniketh Venkat, Attila Gyulassy, Graham Kosiba, Amitesh Maiti, Henry Reinstein, Richard Gee, Peer-Timo Bremer, Valerio Pascucci
External link (DOI)
View presentation:2021-10-27T16:00:00ZGMT-0600Change your timezone on the schedule page
2021-10-27T16:00:00Z
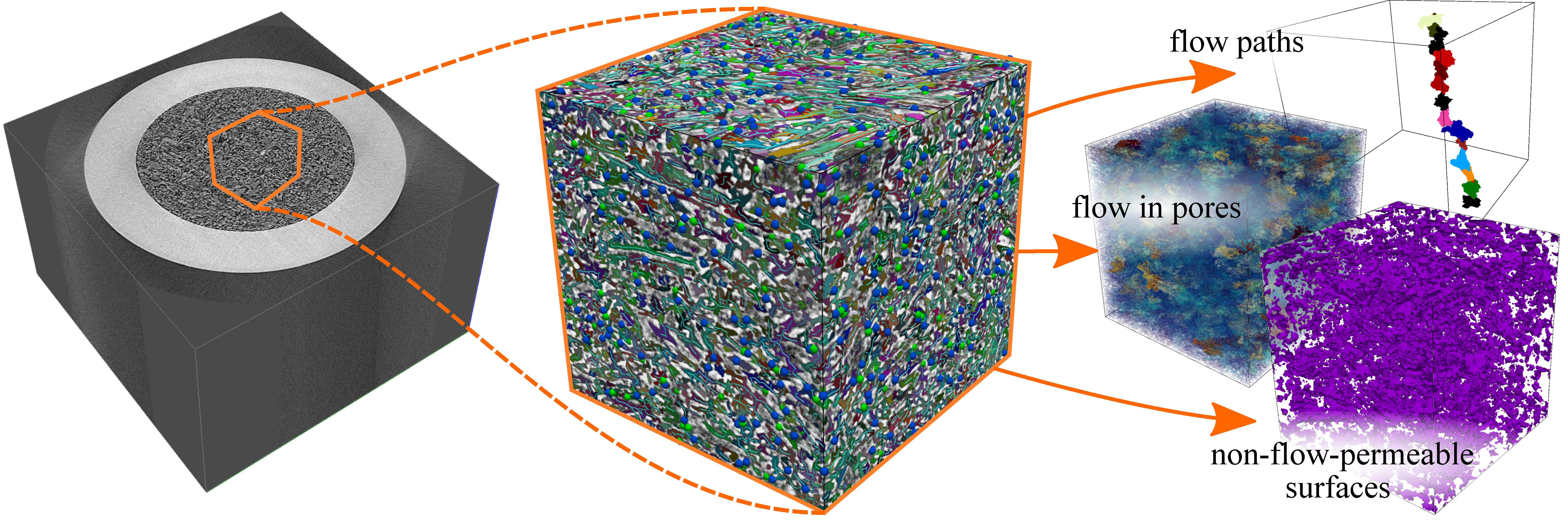
Abstract
In the study of packed granular materials, the performance of a sample (e.g., the detonation of a high-energy explosive) often correlates to measurements of a fluid flowing through it. The “effective surface area,” the surface area accessible to the airflow, is typically measured using a permeametry apparatus that relates the flow conductance to the permeable surface area via the Carman-Kozeny equation. This equation allows calculating the flow rate of a fluid flowing through the granules packed in the sample for a given pressure drop. However, Carman-Kozeny makes inherent assumptions about tunnel shapes and flow paths that may not accurately hold in situations where the particles possess a wide distribution in shapes, sizes, and aspect ratios, as is true with many powdered systems of technological and commercial interest. To address this challenge, we replicate these measurements virtually on micro-CT images of the powdered material, introducing a new Pore Network Model (PNM) based on the skeleton of the Morse-Smale complex. Pores are identified as basins of the complex, their incidence encodes adjacency, and the conductivity of the capillary between them computed from the cross-section at their interface. We build and solve a resistive network to compute an approximate laminar fluid flow through the pore structure. We provide two means of estimating flow-permeable surface area: (i) by direct computation of conductivity, and (ii) by identifying dead-ends in the flow coupled with isosurface extraction and the application of the Carman-Kozeny equation, with the aim of establishing consistency over a range of particle shapes, sizes, porosity levels, and void distribution patterns.