DECE: Decision Explorer with Counterfactual Explanations for Machine Learning Models
Furui Cheng, Yao Ming, Huamin Qu
External link (DOI)
View presentation:2020-10-28T14:45:00ZGMT-0600Change your timezone on the schedule page
2020-10-28T14:45:00Z
Fast forward
Direct link to video on YouTube: https://youtu.be/wVrJ5youWNU
Keywords
Tabular Data, Explainable Machine Learning, Counterfactual Explanation, Decision Making
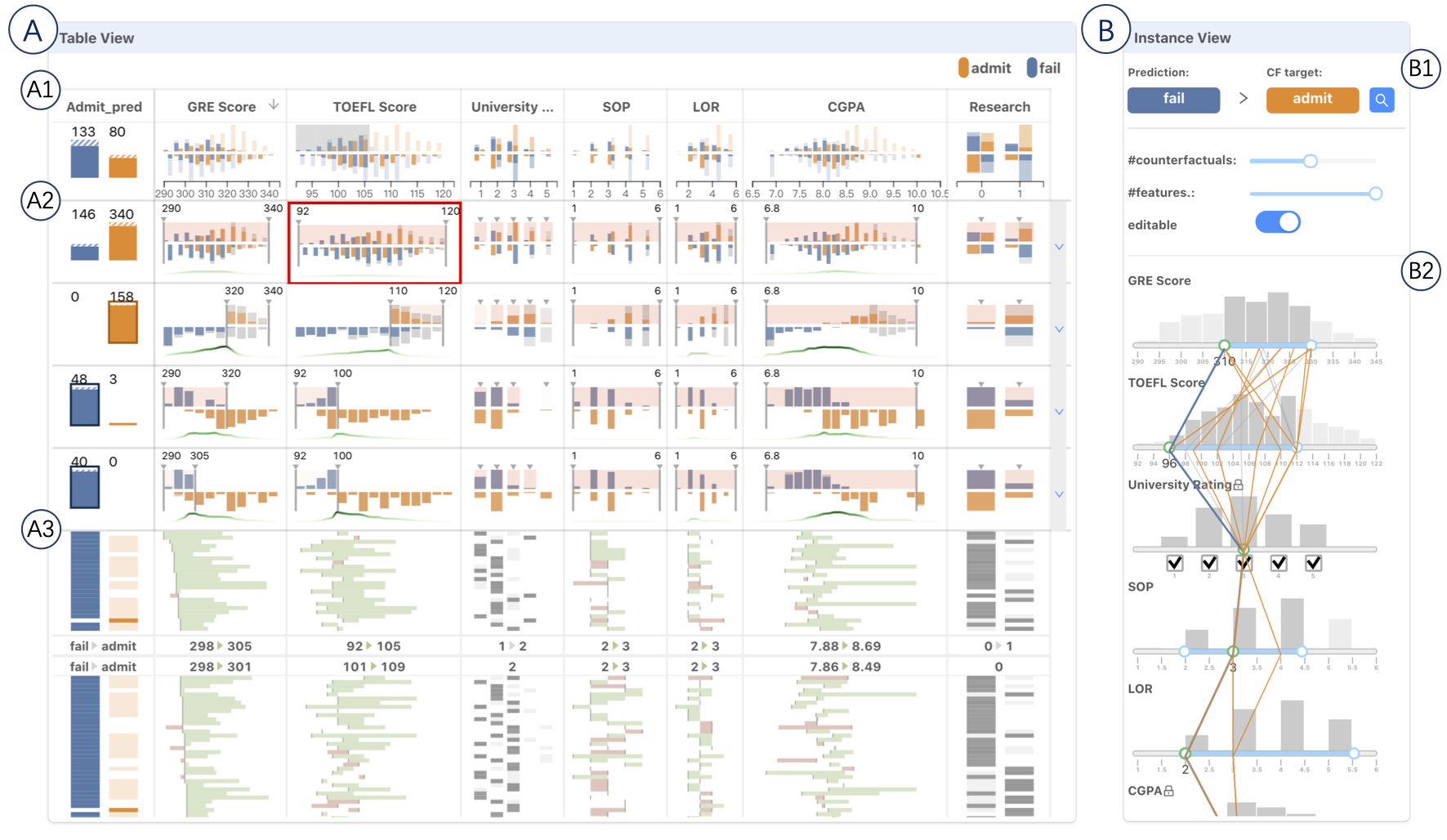
Abstract
With machine learning models being increasingly applied to various decision-making scenarios, people have spent growing efforts to make machine learning models more transparent and explainable. Among various explanation techniques, counterfactual explanations have the advantages of being human-friendly and actionable — a counterfactual explanation tells the user how to gain the desired prediction with minimal changes to the input. Besides, counterfactual explanations can also serve as efficient probes to the models' decisions. In this work, we exploit the potential of counterfactual explanations to understand and explore the behavior of machine learning models. We design DECE, an interactive visualization system that helps understand and explore a model's decisions on individual instances and data subsets, supporting users ranging from decision-subjects to model developers. DECE supports exploratory analysis of model decisions by combining the strengths of counterfactual explanations at instance- and subgroup-levels. We also introduce a set of interactions that enable users to customize the generation of counterfactual explanations to find more actionable ones that can suit their needs. Through three use cases and an expert interview, we demonstrate the effectiveness of DECE in supporting decision exploration tasks and instance explanations.