Force-directed graph layouts revisited: a new force based on the t-Distribution
Fahai Zhong, Mingliang Xue, Jian Zhang, Rui Ban, Oliver Deussen, Yunhai Wang
DOI: 10.1109/TVCG.2023.3238821
Room: 105
2023-10-24T23:57:00ZGMT-0600Change your timezone on the schedule page
2023-10-24T23:57:00Z
Fast forward
Full Video
Keywords
FFT;force directed placement;graph layout;student’s t-distribution
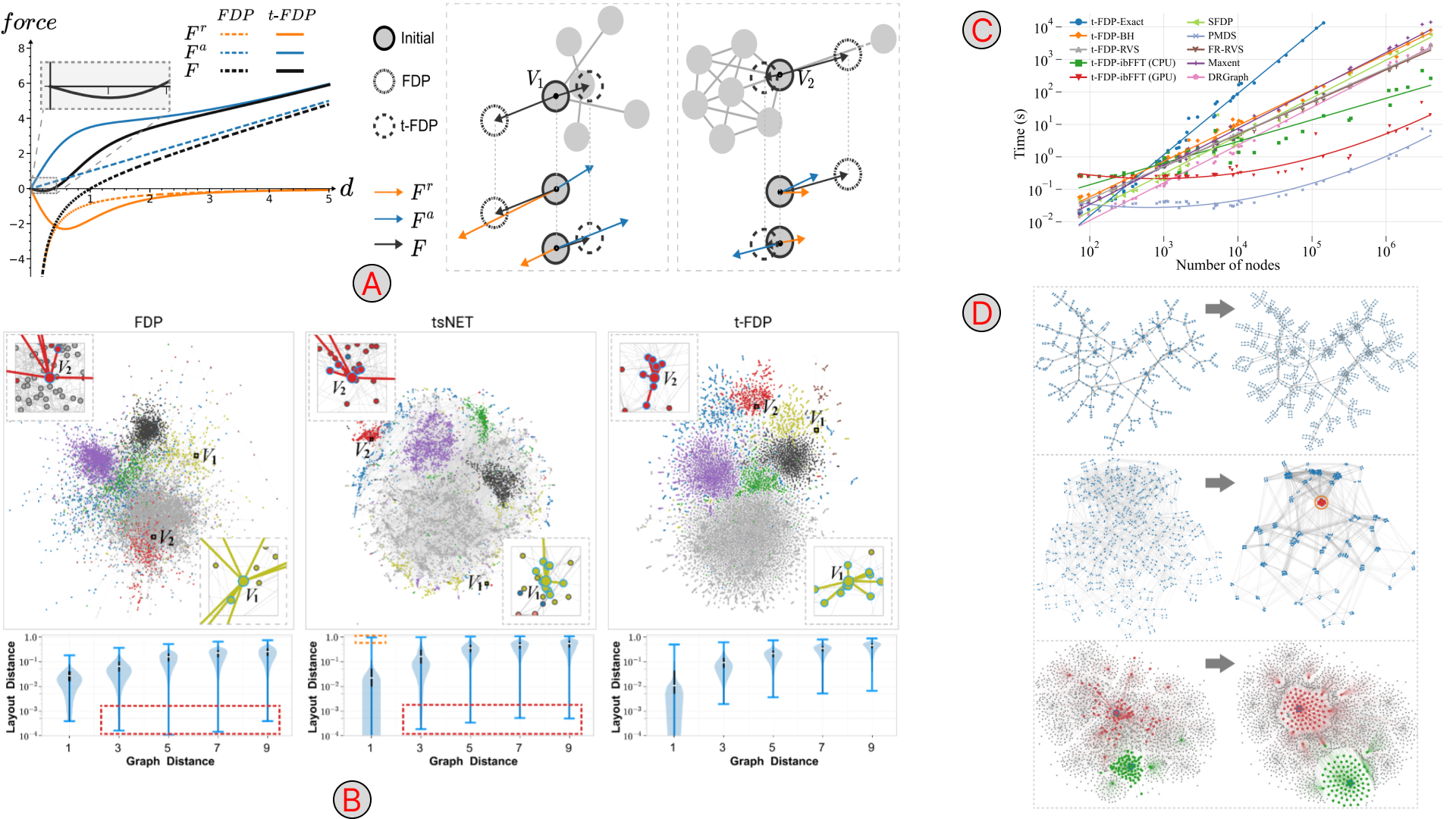
Abstract
In this paper, we propose the t-FDP model, a force-directed placement method based on a novel bounded short-range force (t-force) defined by Student’s t-distribution. Our formulation is flexible, exerts limited repulsive forces for nearby nodes and can be adapted separately in its short- and long-range effects. Using such forces in force-directed graph layouts yields better neighborhood preservation than current methods, while maintaining low stress errors. Our efficient implementation using a Fast Fourier Transform is one order of magnitude faster than state-of-the-art methods and two orders faster on the GPU, enabling us to perform parameter tuning by globally and locally adjusting the t-force in real-time even for complex graphs of up to 10.000 nodes. We demonstrate the quality of our approach by numerical evaluation against state-of-the-art approaches and extensions for interactive exploration.