D-BIAS: A Causality-Based Human-in-the-Loop System for Tackling Algorithmic Bias
Bhavya Ghai, Klaus Mueller
View presentation:2022-10-19T19:24:00ZGMT-0600Change your timezone on the schedule page
2022-10-19T19:24:00Z
Prerecorded Talk
The live footage of the talk, including the Q&A, can be viewed on the session page, Questioning Data and Data Bias.
Fast forward
Abstract
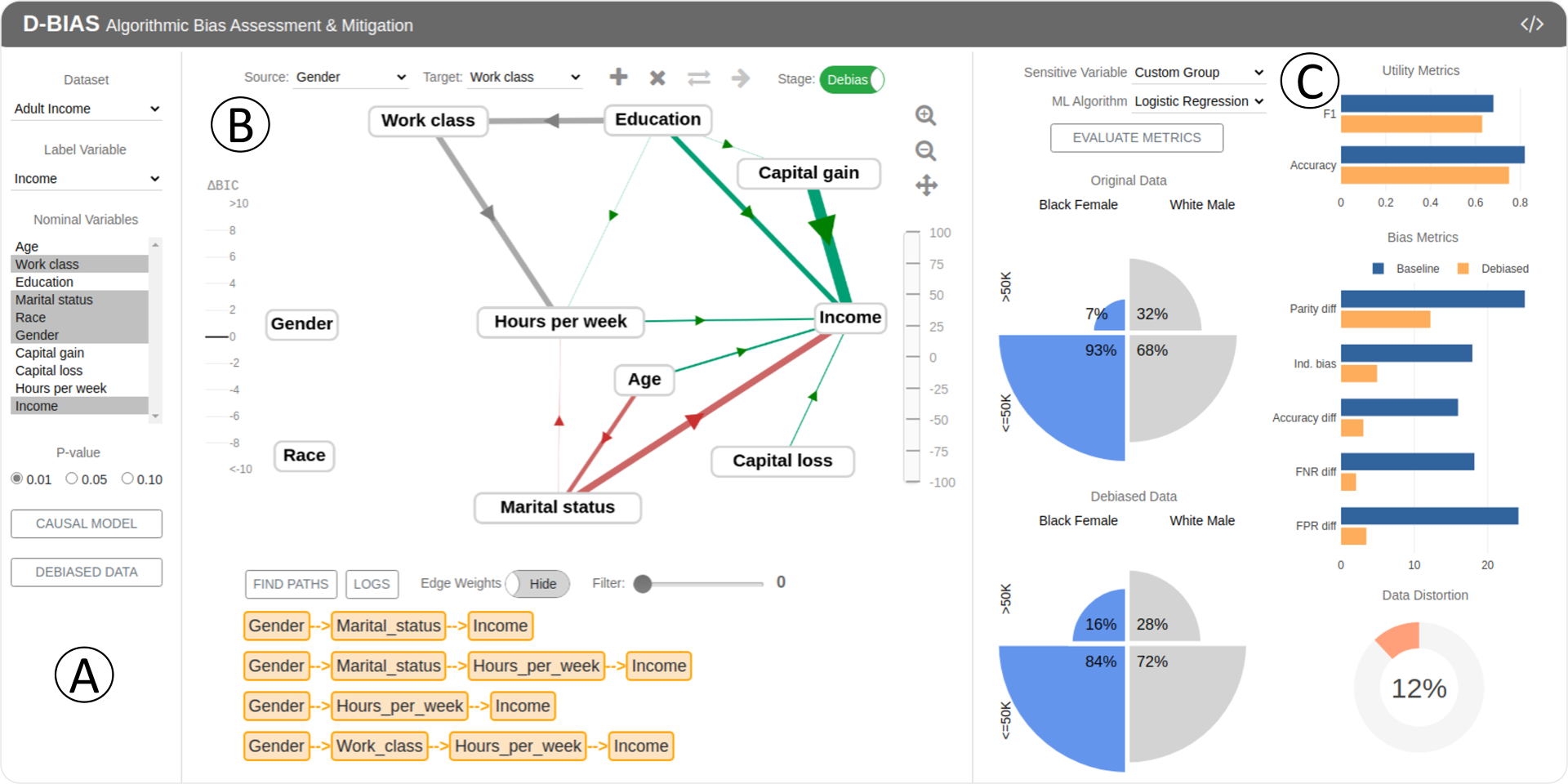
With the rise of AI, algorithms have become better at learning underlying patterns from the training data including ingrained social biases based on gender, race, etc. Deployment of such algorithms to domains such as hiring, healthcare, law enforcement, etc. has raised serious concerns about fairness, accountability, trust and interpretability in machine learning algorithms. To alleviate this problem, we propose D-BIAS, a visual interactive tool that embodies human-in-the-loop AI approach for auditing and mitigating social biases from tabular datasets. It uses a graphical causal model to represent causal relationships among different features in the dataset and as a medium to inject domain knowledge. A user can detect the presence of bias against a group, say females, or a subgroup, say black females, by identifying unfair causal relationships in the causal network and using an array of fairness metrics. Thereafter, the user can mitigate bias by refining the causal model and acting on the unfair causal edges. For each interaction, say weakening/deleting a biased causal edge, the system uses a novel method to simulate a new (debiased) dataset based on the current causal model while ensuring a minimal change from the original dataset. Users can visually assess the impact of their interactions on different fairness metrics, utility metrics, data distortion, and the underlying data distribution. Once satisfied, they can download the debiased dataset and use it for any downstream application for fairer predictions. We evaluate D-BIAS by conducting experiments on 3 datasets and also a formal user study. We found that D-BIAS helps reduce bias significantly compared to the baseline debiasing approach across different fairness metrics while incurring little data distortion and a small loss in utility. Moreover, our human-in-the-loop based approach significantly outperforms an automated approach on trust, interpretability and accountability.