Effects of View Layout On Situated Analytics for Multiple-View Representations in Immersive Visualization
Zhen Wen, Wei Zeng, Luoxuan Weng, Yihan Liu, Mingliang Xu, Wei Chen
View presentation:2022-10-19T19:36:00ZGMT-0600Change your timezone on the schedule page
2022-10-19T19:36:00Z
Prerecorded Talk
The live footage of the talk, including the Q&A, can be viewed on the session page, Immersive Analytics and Situated Visualization.
Fast forward
Abstract
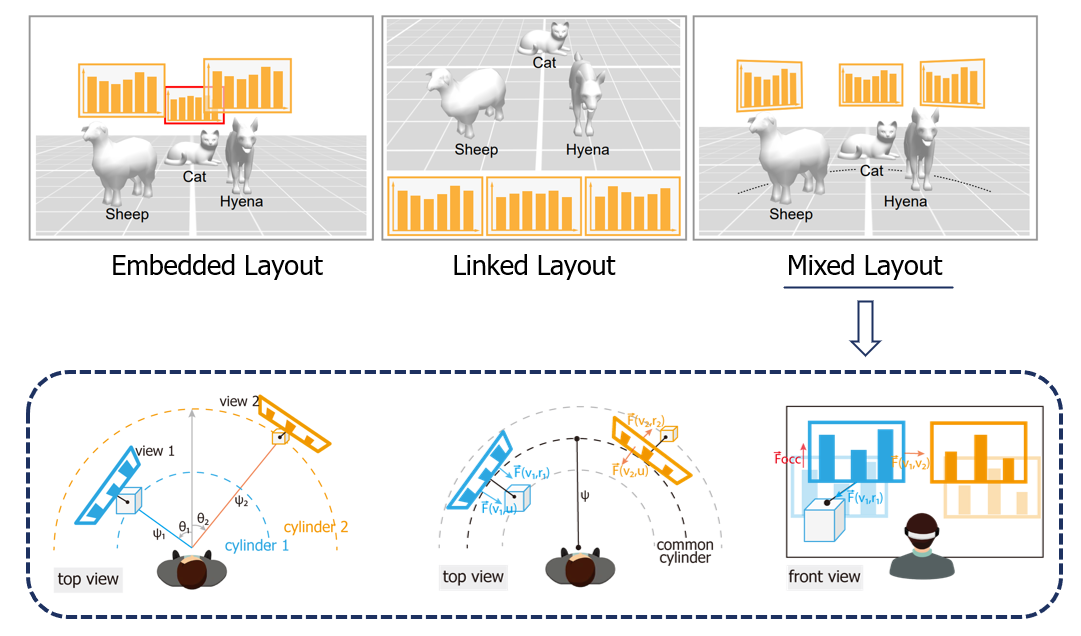
Multiple-view (MV) representations enabling multi-perspective exploration of large and complex data are often employed on 2D displays. The technique also shows great potential in addressing complex analytic tasks in immersive visualization. However, although useful, the design space of MV representations in immersive visualization lacks in deep exploration. In this paper, we propose a new perspective to this line of research, by examining the effects of view layout for MV representations on situated analytics. Specifically, we disentangle situated analytics in perspectives of situatedness regarding spatial relationship between visual representations and physical referents, and analytics regarding cross-view data analysis including filtering, refocusing, and connecting tasks. Through an in-depth analysis of existing layout paradigms, we summarize design trade-offs for achieving high situatedness and effective analytics simultaneously. We then distill a list of design requirements for a desired layout that balances situatedness and analytics, and develop a prototype system with an automatic layout adaptation method to fulfill the requirements. The method mainly includes a cylindrical paradigm for egocentric reference frame, and a force-directed method for proper view-view, view-user, and view-referent proximities and high view visibility. We conducted a formal user study that compares layouts by our method with linked and embedded layouts. Quantitative results show that participants finished filtering- and connecting-centered tasks significantly faster with our layouts, and user feedback confirms high usability of the prototype system.