RMExplorer: A Visual Analytics Approach to Explore the Performance and the Fairness of Disease Risk Models on Population Subgroups
Bum Chul Kwon, Uri Kartoun, Shaan Khurshid, Mikhail Yurochkin, Subha Maity, Deanna G Brockman, Amit V Khera, Patrick T Ellinor, Steven A Lubitz, Kenney Ng
View presentation:2022-10-19T20:54:00ZGMT-0600Change your timezone on the schedule page
2022-10-19T20:54:00Z
Prerecorded Talk
The live footage of the talk, including the Q&A, can be viewed on the session page, Visual Analytics, Decision Support, and Machine Learning.
Fast forward
Keywords
visual analytics, health informatics, fairness, subgroup analysis, explainability, interpretability, electronic health records
Abstract
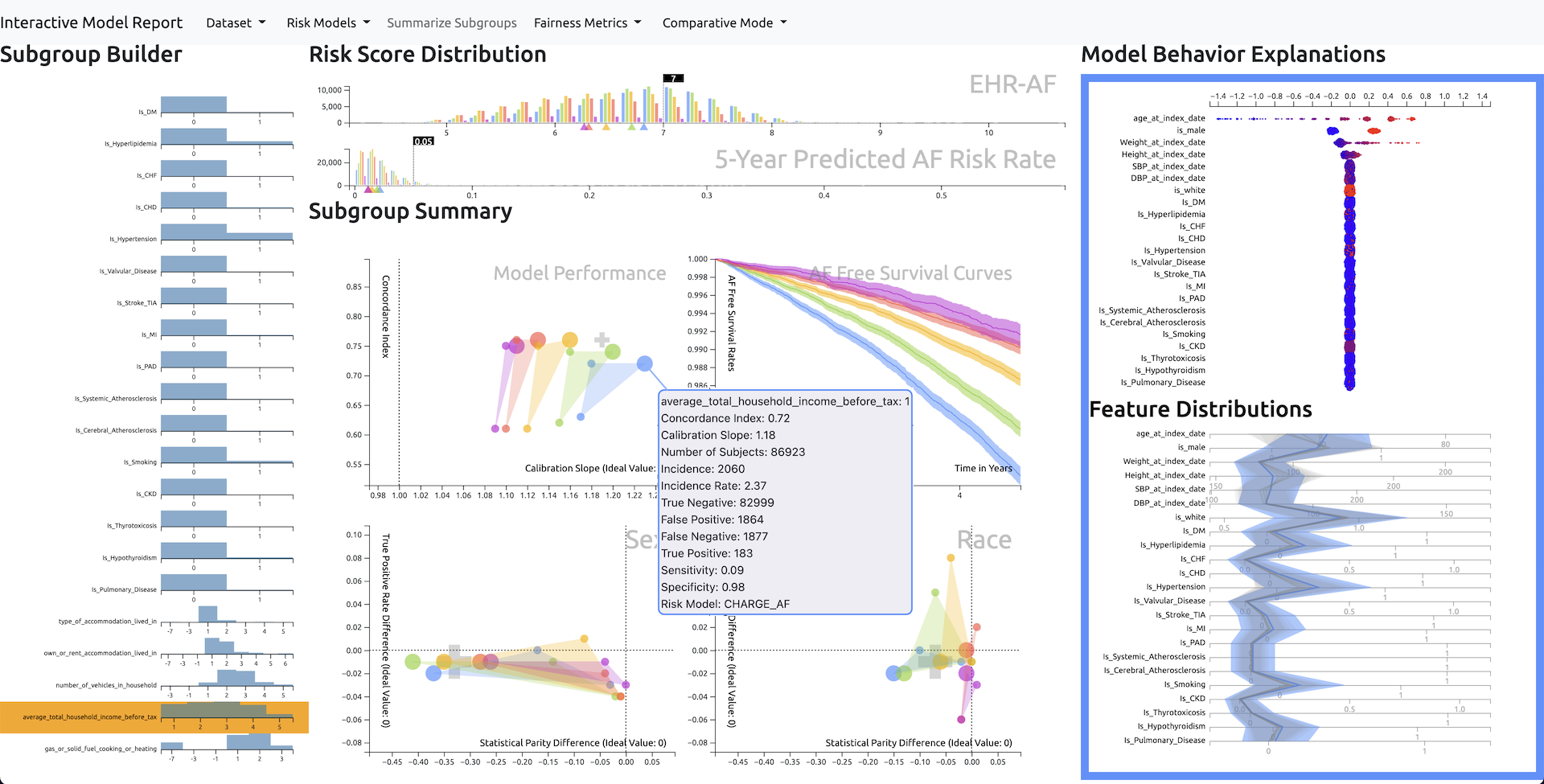
Disease risk models can identify high-risk patients and help clinicians provide more personalized care. However, risk models developed on one dataset may not generalize across diverse subpopulations of patients in different datasets and may have unexpected performance. It is challenging for clinical researchers to inspect risk models across different subgroups without any tools. Therefore, we developed an interactive visualization system called RMExplorer (Risk Model Explorer) to enable interactive risk model assessment. Specifically, the system allows users to define subgroups of patients by selecting clinical, demographic, or other characteristics, to explore the performance and fairness of risk models on the subgroups, and to understand the feature contributions to risk scores. To demonstrate the usefulness of the tool, we conduct a case study, where we use RMExplorer to explore three atrial fibrillation risk models by applying them to the UK Biobank dataset of 445,329 individuals. RMExplorer can help researchers to evaluate the performance and biases of risk models on subpopulations of interest in their data.