Autoencoder-Aided Visualization of Collections of Morse Complexes
Jixian Li, Dan Van Boxel, Joshua Levine
View presentation:2022-10-17T20:45:00ZGMT-0600Change your timezone on the schedule page
2022-10-17T20:45:00Z
The live footage of the talk, including the Q&A, can be viewed on the session page, TopoInVis: Session 2, Early Career Lightning Talks + Best Paper Awards .
Keywords
Morse complex, Dimensionality reduction, Autoencoders
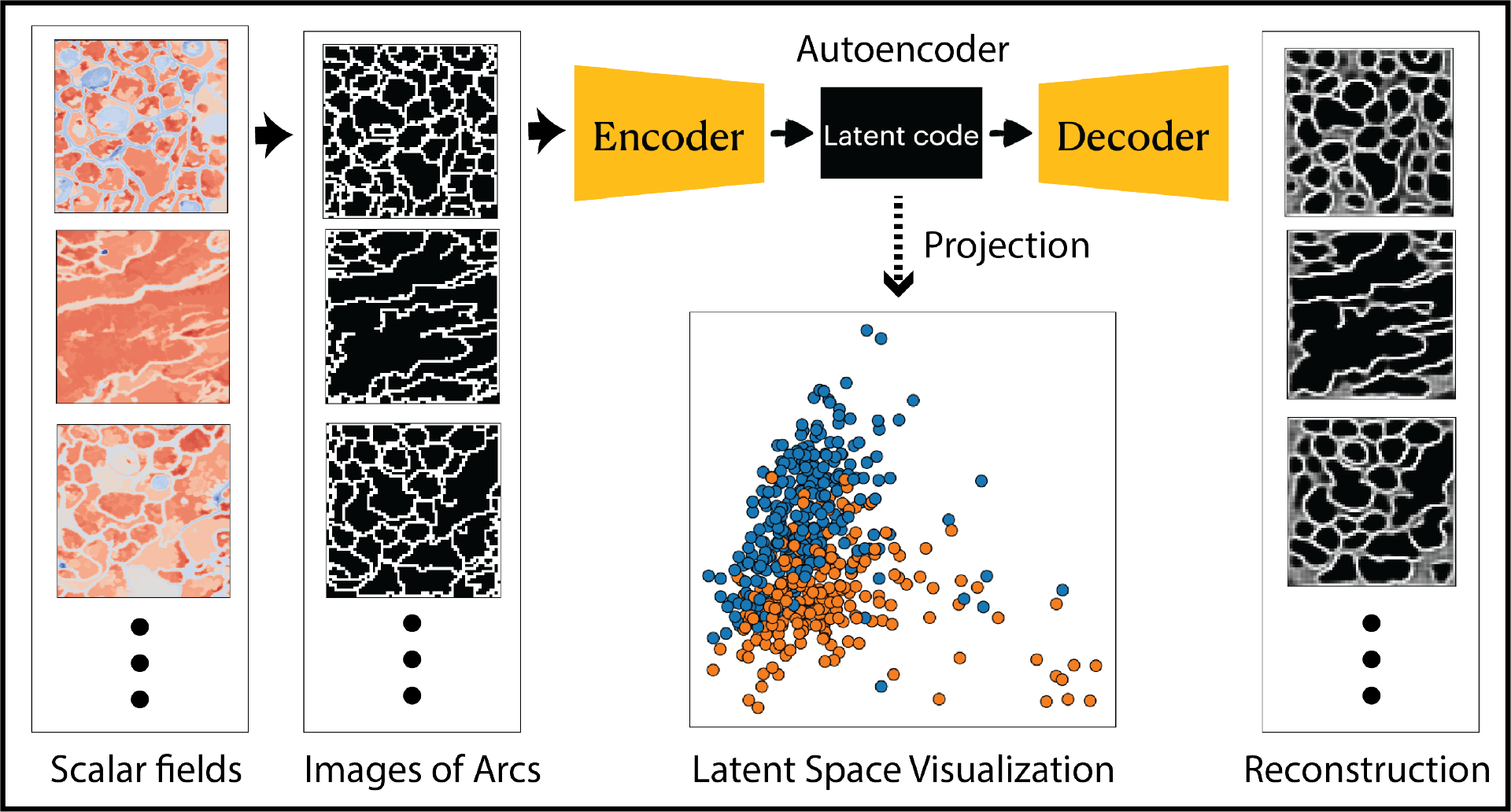
Abstract
Though analyzing a single scalar field using Morse complexes is well studied, there are few techniques for visualizing a collection of Morse complexes. We focus on analyses that are enabled by looking at a Morse complex as an embedded domain decomposition. Specifically, we target 2D scalar fields, and we encode the Morse complex through binary images of the boundaries of decomposition. Then we use image-based autoencoders to create a feature space for the Morse complexes. We apply additional dimensionality reduction methods to construct a scatterplot as a visual interface of the feature space. This allows us to investigate individual Morse complexes, as they relate to the collection, through interaction with the scatterplot. We demonstrate our approach using a synthetic data set, microscopy images, and time-varying vorticity magnitude fields of flow. Through these, we show that our method can produce insights about structures within the collection of Morse complexes.